What is the Difference Between Forced Air and Heat Pumps?
If you’re in the market for a new heating system or are considering an upgrade, you may have come across the terms “forced air” and “heat pump.” While both are common heating options, they operate differently and have distinct advantages. In this blog post, we will explore the differences between forced air systems and heat pumps so that you can decide which option is best suited for your needs.
Understanding Forced Air Systems
A forced air heating system is one of the most popular and widely used heating methods in residential and commercial buildings. It works by using a furnace to generate heat, which is then distributed throughout the building via a network of ducts. The warm air is propelled by a blower fan, which pushes it through the ductwork and out of the vents into each room.
Forced air systems are known for their efficiency and ability to quickly heat up a space. They are often paired with central air conditioning systems, as the same ductwork can be used for heating and cooling. This versatility makes forced air systems popular among homeowners looking for a comprehensive heating and cooling solution.
Introducing Heat Pumps
On the other hand, heat pumps work differently than forced air systems. They are designed to transfer heat from one location to another rather than generating heat themselves. Depending on the season, heat pumps can be used for heating and cooling purposes.
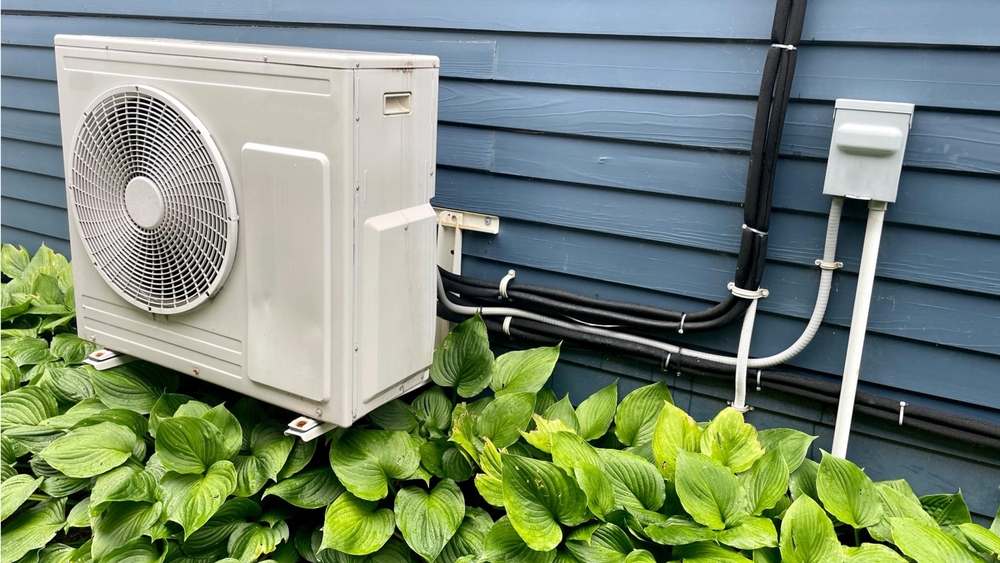
Heat pumps extract heat from the air, ground, or water sources outside the building and then transfer it inside using a refrigeration cycle. In heating mode, the heat pump absorbs heat energy from the outdoor air and releases it indoors. In cooling mode, the process is reversed, with the heat pump extracting heat from the inside and expelling it outside.
Air-Source Heat Pumps
Air-source heat pumps are the most common among the various types of heat pumps. They use the outdoor air as the heat source in winter and as the heat sink in summer. Air-source heat pumps offer several advantages: energy efficiency, cost savings, and environmental friendliness.
One of the key benefits of air-source heat pumps is their high energy efficiency. Unlike forced air systems, which generate heat through combustion or electrical resistance, air-source heat pumps simply transfer heat, requiring less energy to do so. This results in lower energy bills and reduced carbon emissions, making them an environmentally friendly choice.
Another advantage of air-source heat pumps is their cost-effectiveness. While the upfront installation cost may be higher than traditional forced air systems, the long-term savings can outweigh the initial investment. With proper maintenance and usage, air-source heat pumps can significantly lower your heating and cooling costs, leading to substantial savings over time.
Choosing the Right System for Your Needs
When deciding between a forced air system and a heat pump, there are several factors to consider. One crucial factor is your specific climate and local weather conditions. Air-source heat pumps are suitable for regions with moderate climates, where the temperature rarely drops below freezing. Heat pumps may struggle to extract sufficient heat from the air in colder climates, resulting in reduced efficiency.
Additionally, the size of your home or building plays a role in determining which system is best for you. Larger spaces may benefit from the distribution capabilities of a forced air system, which can quickly and effectively heat or cool the entire area. Smaller homes or apartments might find air-source heat pumps more suitable, as they offer zoned heating and cooling options, allowing you to adjust temperatures in different areas.
Lastly, your budget and long-term cost considerations are essential. Forced air systems may have lower initial costs, but ongoing maintenance and energy expenses could add up over time. While pricier upfront, air-source heat pumps offer significant long-term savings and efficiency benefits. Consider your budget and energy consumption goals carefully when making a decision.
Contact Us Today
Choosing the right heating system for your home or business is crucial to impacting your comfort and energy costs. If you’re still unsure whether a forced air system or a heat pump is the right choice, contact the HVAC experts at PlumbSmart. With years of experience in the industry, our knowledgeable technicians can assess your specific needs and recommend the most suitable heating solution.
Contact us to learn more about our services and schedule a consultation. Don’t let winter catch you off guard – make an informed decision today and ensure your home or business is cozy and energy-efficient all year round.